
What is the Cold War?
The Cold War was a state of political and military tension between the United States of America (USA) and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) that lasted from the end of World War II in 1945 until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. The term "Cold War" was coined by journalist Walter Lippmann in 1947 to describe the hostility and rivalry that existed between the two superpowers without direct military conflict.
Origins of the Cold War

The origins of the Cold War can be traced back to the Yalta Conference in February 1945, where the leaders of the three major Allied powers - Franklin D. Roosevelt of the USA, Winston Churchill of Great Britain, and Joseph Stalin of the USSR - met to discuss the post-war reorganization of Europe. The conference highlighted the ideological and geopolitical differences between the two superpowers, with the USA advocating for democracy and capitalism and the USSR advocating for communism and socialism.
The Iron Curtain

In March 1946, Winston Churchill delivered his famous "Iron Curtain" speech in Fulton, Missouri, in which he warned of the division of Europe into two hostile camps - one led by the USA and the other by the USSR - and the need for the Western powers to stand firm against Soviet aggression. The term "Iron Curtain" became a symbol of the division between East and West during the Cold War.
The Truman Doctrine

In March 1947, President Harry S. Truman announced the Truman Doctrine, which provided military and economic aid to countries threatened by communism. The Truman Doctrine was a response to the Soviet Union's attempts to spread communism beyond its borders and marked the beginning of an era of American interventionism in world affairs.
The Marshall Plan
In June 1947, Secretary of State George Marshall announced the Marshall Plan, which provided economic assistance to Western European countries devastated by World War II. The Marshall Plan was designed to help rebuild the economies of Europe and prevent the spread of communism by creating stable, prosperous democracies.
The Berlin Blockade

In June 1948, the Soviet Union blockaded the Western-controlled sectors of Berlin in an attempt to force the Western powers to abandon their positions in the city. The Berlin Blockade was a major crisis in the early years of the Cold War and led to the Berlin Airlift, in which the USA and its allies airlifted supplies to the city.
The Korean War

In June 1950, North Korea invaded South Korea and sparked the Korean War, which lasted until July 1953. The Korean War was the first major conflict of the Cold War and saw the intervention of both the USA and the Soviet Union.
The Cuban Missile Crisis
In October 1962, the USA discovered that the Soviet Union had placed nuclear missiles in Cuba, just 90 miles from the US coast. The Cuban Missile Crisis was a major crisis in the Cold War and brought the world closer to nuclear war than ever before. The crisis was resolved when the Soviet Union agreed to remove the missiles in exchange for a US pledge not to invade Cuba and the removal of US missiles from Turkey.
The Vietnam War

The Vietnam War was a major conflict in Southeast Asia that lasted from 1955 to 1975. The war was fought between the communist government of North Vietnam and the government of South Vietnam, which was supported by the USA and other anti-communist allies. The Vietnam War was one of the most controversial and divisive conflicts in American history and led to widespread protests and anti-war movements.
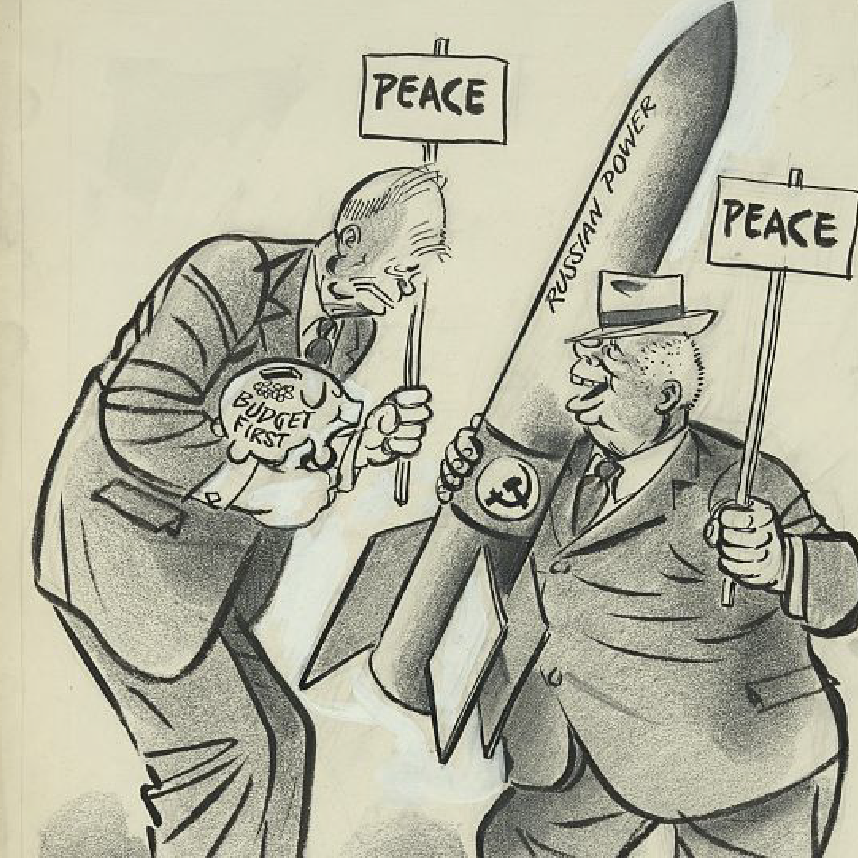
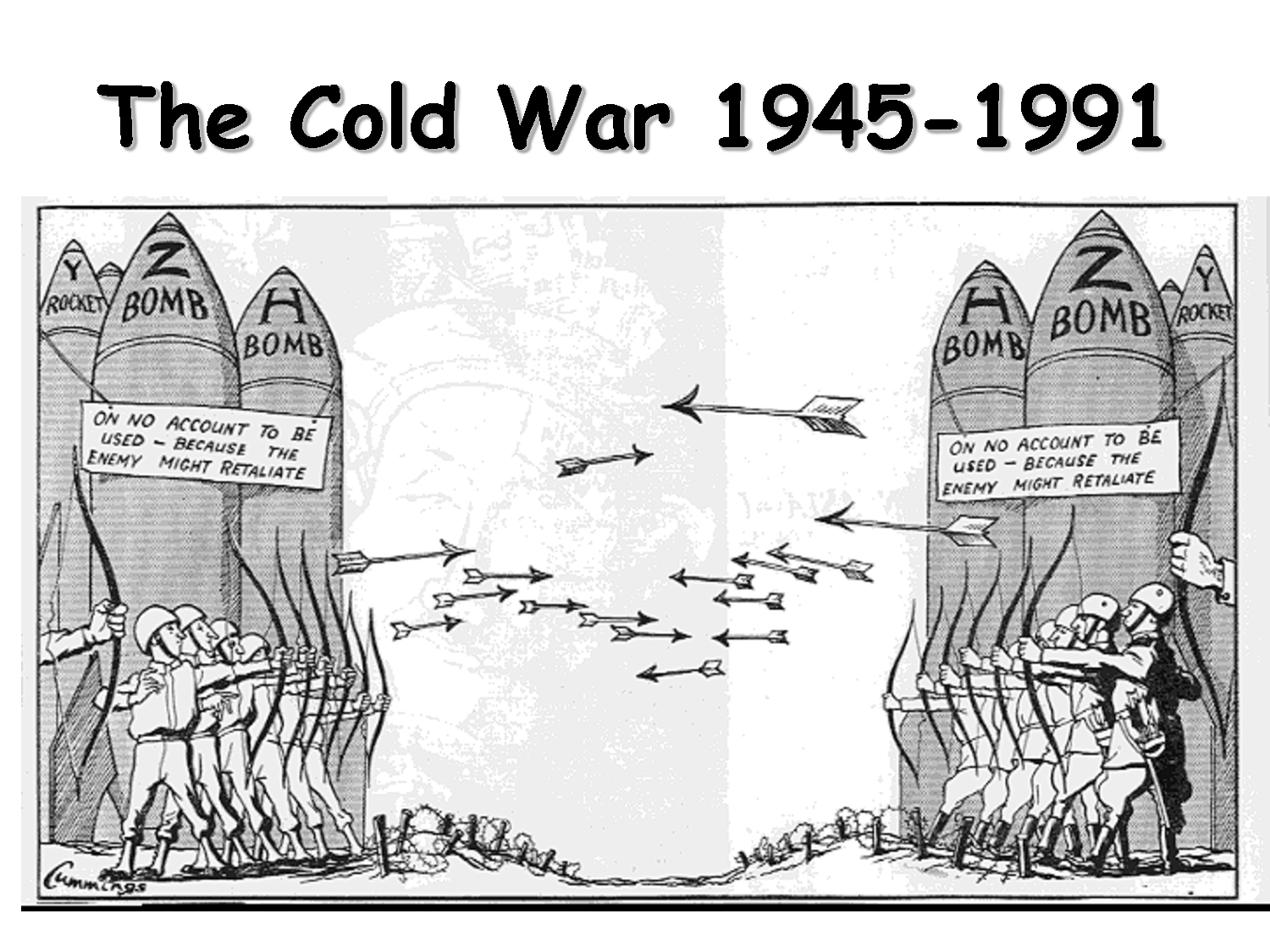
The Arms Race
The Cold War was marked by a massive arms race between the USA and the Soviet Union, with both sides developing and stockpiling nuclear weapons and other military technology. The arms race was fueled by a mutual fear and distrust between the two superpowers and led to a dangerous escalation of tensions.
The Space Race
The Space Race was a competition between the USA and the Soviet Union to achieve milestones in space exploration and technology. The Space Race was a key component of the Cold War and saw both sides investing heavily in space programs, including the Soviet Union's launch of the first satellite, Sputnik, in 1957, and the USA's landing of a man on the moon in 1969.
The End of the Cold War

The Cold War came to an end with the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. The Soviet Union had been experiencing economic and political turmoil for years, and the reforms of Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev failed to save the system. The collapse of the Soviet Union marked the end of the bipolar world order that had dominated international relations since World War II.
Conclusion
The Cold War was a defining period in world history that shaped the political, economic, and military landscape of the 20th century. The rivalry between the USA and the Soviet Union had far-reaching consequences, including the establishment of a global arms race, the development of new technologies, and the emergence of new superpowers. Although the Cold War is long over, its legacy continues to shape international relations and global politics today.